 a given angle in quadrant 2" width="1280" height="1280" />
a given angle in quadrant 2" width="1280" height="1280" />Use our reference angle calculator to find the reference angle for any angle in degrees or radians.
 a given angle in quadrant 2" width="1280" height="1280" />
a given angle in quadrant 2" width="1280" height="1280" />

Joe is the creator of Inch Calculator and has over 20 years of experience in engineering and construction. He holds several degrees and certifications.
Review Badge Icon Reviewed by Pateakia Heath, PhD
Pateakia has worked in education for 15 years and has three degrees, including a PhD, Master's degree, and Bachelor's degree. She specializes in mathematics.
Sexton, J. (n.d.). Reference Angle Calculator. Inch Calculator. Retrieved September 4, 2024 , from https://www.inchcalculator.com/reference-angle-calculator/
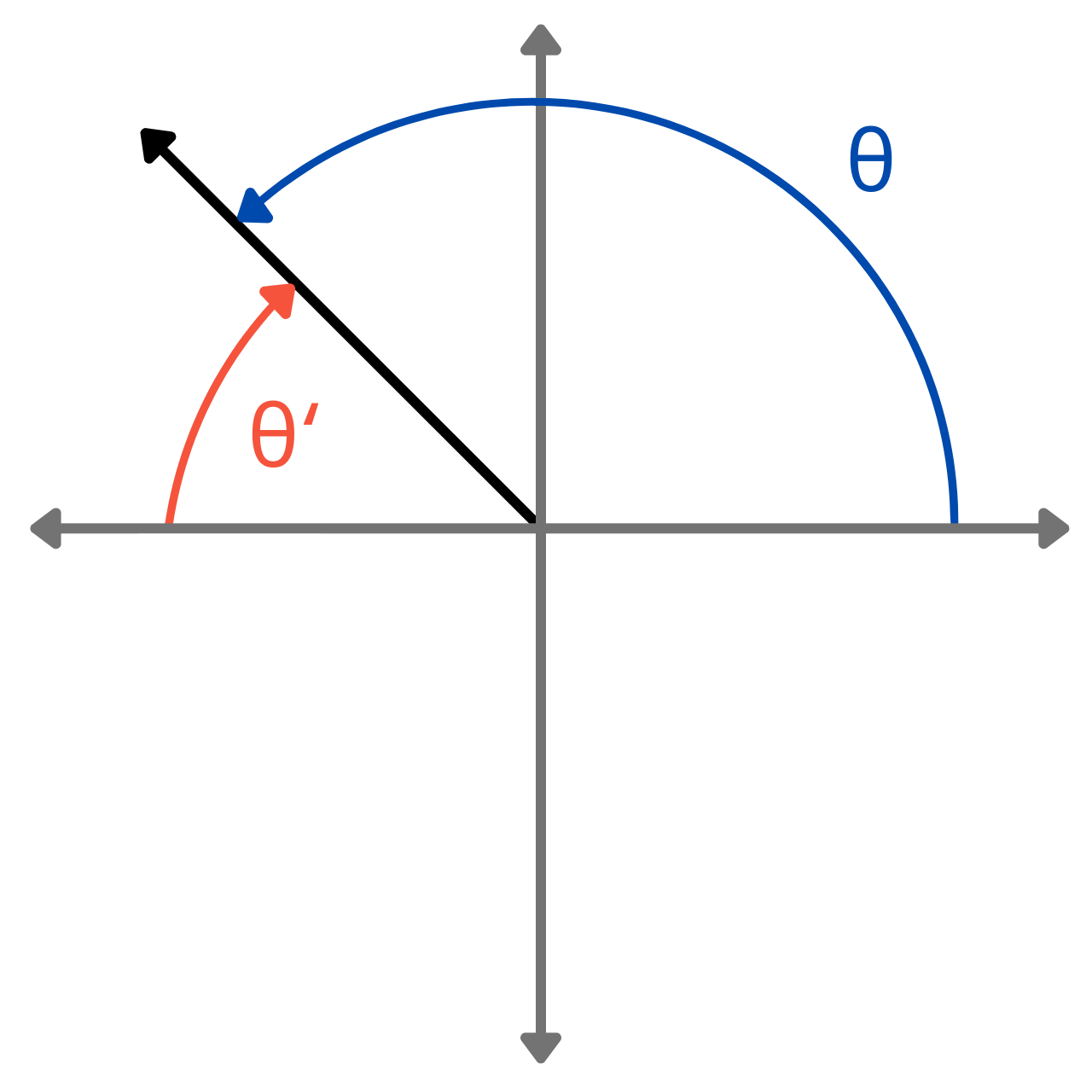
A reference angle is the acute angle formed between the terminal side of an angle in standard position and the x-axis. It serves as a reference point to determine the exact values of trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent.
Reference angles are used to simplify complex calculations and reduce problems to a manageable form.
The graphic below illustrates the reference angle for various angles in each quadrant.
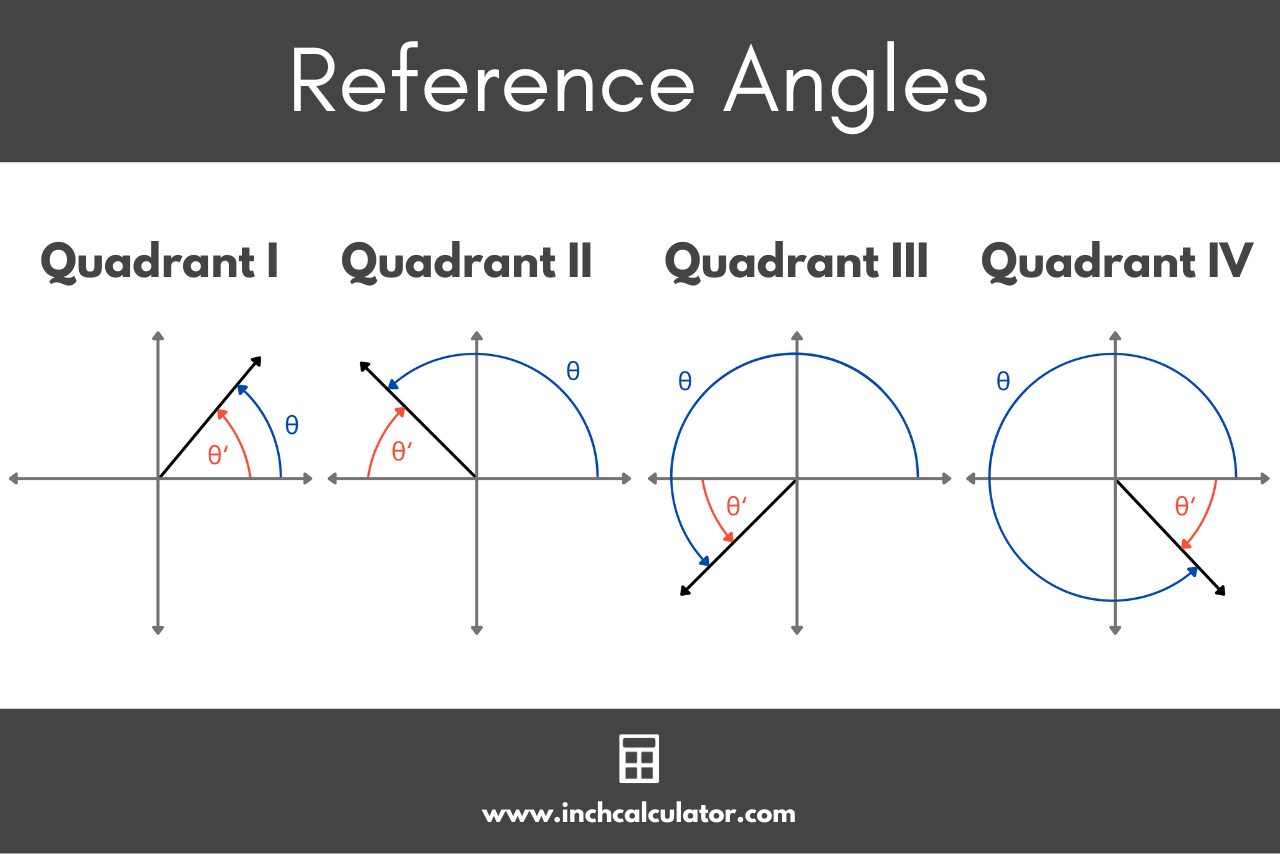
Reference angles are particularly useful when evaluating trigonometric functions on the unit circle or solving trigonometric equations.
You can find the reference angle using a formula.
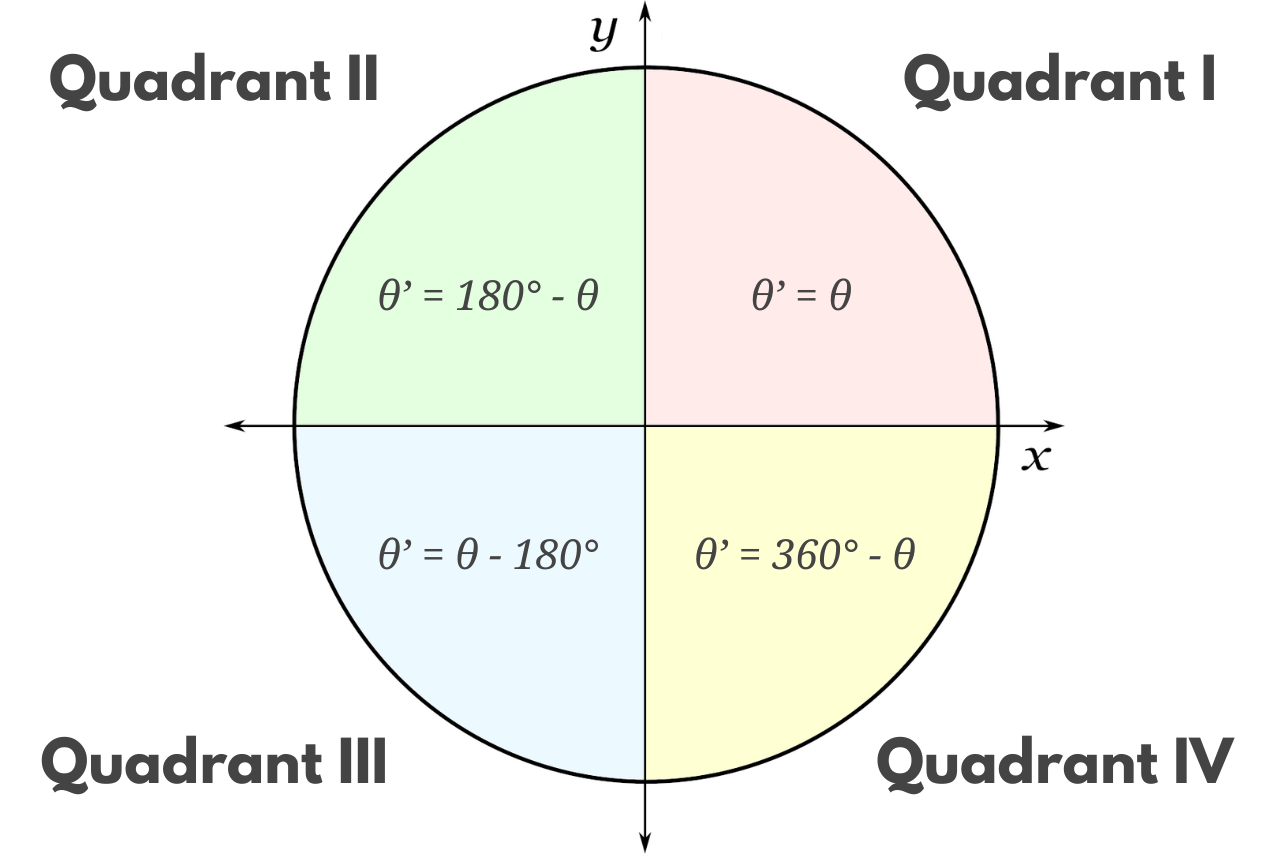
The formula to calculate the reference angle varies depending on which quadrant the terminal side of the angle lies.
The following table shows which quadrant an angle is in.
If the angle θ is in quadrant I, then the reference angle θ’ is equal to the angle θ.
If the angle θ is in quadrant II, then the reference angle θ’ is equal to 180° minus the angle θ.
If the angle θ is in quadrant III, then the reference angle θ’ is equal to the angle θ minus 180°.
If the angle θ is in quadrant IV, then the reference angle θ’ is equal to 360° minus the angle θ.
You can use our degrees to radians converter to determine the quadrant for an angle in radians.
It’s important to note that reference angles are always positive, regardless if the original angle is positive or negative. This means that a reference angle will always be equal to the absolute value of the result of the formulas above.
You may also be interested in our coterminal angle calculator.
| Angle | Reference Angle |
|---|---|
| 0° | 0° |
| 5° | 5° |
| 10° | 10° |
| 15° | 15° |
| 20° | 20° |
| 25° | 25° |
| 30° | 30° |
| 35° | 35° |
| 40° | 40° |
| 45° | 45° |
| 50° | 50° |
| 55° | 55° |
| 60° | 60° |
| 65° | 65° |
| 70° | 70° |
| 75° | 75° |
| 80° | 80° |
| 85° | 85° |
| 90° | 90° |
| 95° | 85° |
| 100° | 80° |
| 105° | 75° |
| 110° | 70° |
| 115° | 65° |
| 120° | 60° |
| 125° | 55° |
| 130° | 50° |
| 135° | 45° |
| 140° | 40° |
| 145° | 35° |
| 150° | 30° |
| 155° | 25° |
| 160° | 20° |
| 165° | 15° |
| 170° | 10° |
| 175° | 5° |
| 180° | 0° |
| 185° | 5° |
| 190° | 10° |
| 195° | 15° |
| 200° | 20° |
| 205° | 25° |
| 210° | 30° |
| 215° | 35° |
| 220° | 40° |
| 225° | 45° |
| 230° | 50° |
| 235° | 55° |
| 240° | 60° |
| 245° | 65° |
| 250° | 70° |
| 255° | 75° |
| 260° | 80° |
| 265° | 85° |
| 270° | 90° |
| 275° | 85° |
| 280° | 80° |
| 285° | 75° |
| 290° | 70° |
| 295° | 65° |
| 300° | 60° |
| 305° | 55° |
| 310° | 50° |
| 315° | 45° |
| 320° | 40° |
| 325° | 35° |
| 330° | 30° |
| 335° | 25° |
| 340° | 20° |
| 345° | 15° |
| 350° | 10° |
| 355° | 5° |
| 360° | 0° |
You can find the reference angle for an angle in radians by converting your radians to degrees and then solving for the reference angle. The formula to convert radians to degrees is radians times 180 divided by pi.
Reference angles serve as a reference point to determine the exact values of trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent.
The reference angle for 150° is 30°.